Psychology Class: The Complex Relationship Between Teenage Social Media Use, Anxiety, and Depression
Understanding the psychological impact of social media on teenagers is becoming increasingly important in our digital age. This article delves into the findings of recent research, shedding light on the link between social media usage and mental health outcomes such as anxiety and depression among teenagers. Recognizing social media's pervasive influence, we explore the contributing factors, potential solutions, and the critical areas for future research in understanding adolescents' mental health challenges.
Specification of the Study
The study discussed here falls under the fields of psychopathology and research methods. It examines the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes, drawing from extensive data over a decade. The research uses correlational data to uncover potential links while highlighting the limitations of such an approach.
Correlational Data: Understanding the Limitations
One of the key insights from the research is the relationship between social media use and mental health problems like anxiety and depression in teenagers. However, it's crucial to understand that correlational data can point to a relationship but does not establish a cause-and-effect link. This means that while social media use might be associated with mental health issues, it does not necessarily cause them. Factors such as pre-existing mental health issues or external stressors might also drive teenagers to spend more time on social media.
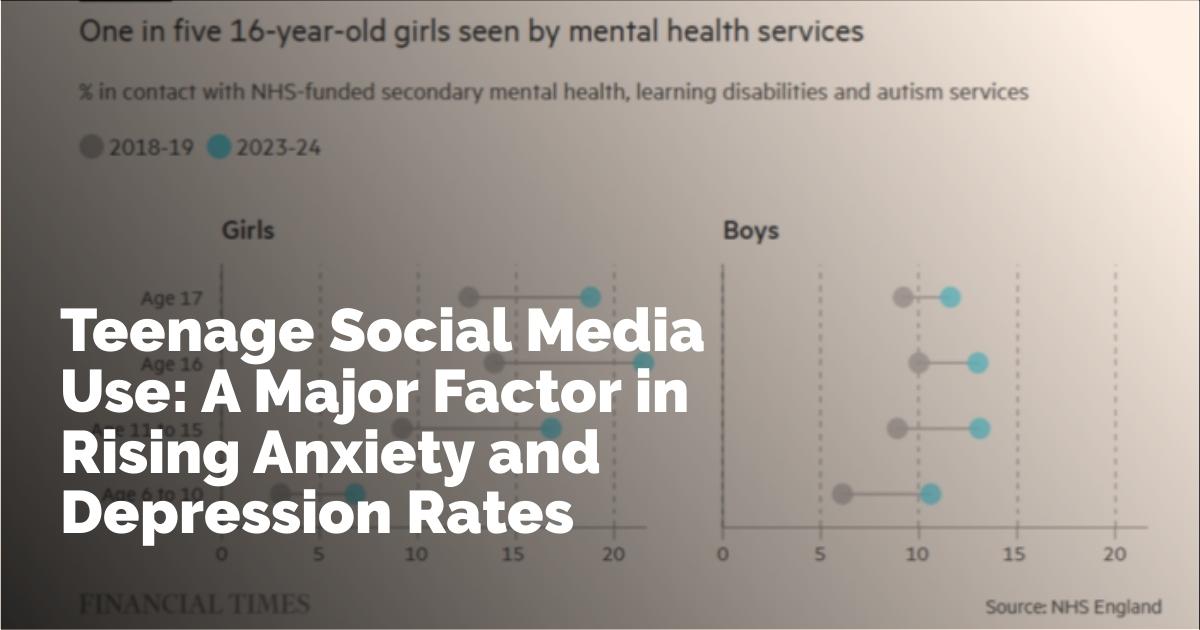
Gender Discrepancies in Reported Mental Health Issues
The study also indicates that girls report more mental health issues compared to boys, signaling the need to explore the underlying psychological and sociocultural factors. Girls may face different societal pressures, such as more significant expectations concerning appearance and social engagement. They might also be more adept at expressing emotions, leading to higher reports of mental challenges. Understanding these dynamics is essential for tailoring support appropriately.
Improving Mental Health Through Sleep and Exercise
The study concludes that enhancing sleep and exercise could significantly benefit teenagers' mental health. From a psychological perspective, regular physical activity and adequate rest have profound effects on mental well-being. Physical exercise releases endorphins, which are chemicals in the brain that act as natural mood lifters. Furthermore, sleep is crucial for cognitive functioning and emotional regulation, helping to reduce stress and mood disorders.
Impact of Social Media Platforms on Teen Mental Health
The design and culture of the most popular social media platforms can significantly affect teenage mental health. Features like "likes," comments, and the visibility of followers can create competitive environments where self-esteem is constantly evaluated against peers. Additionally, the algorithm-driven content feeds that prioritize sensational or emotionally charged content can contribute to heightened anxiety and mood swings.
Research Methodology: Longitudinal Studies
The study utilized longitudinal research methods to examine participants' mental health trajectories over ten years. A longitudinal study's strength is its ability to observe changes and developments over time, providing a comprehensive view of trends and patterns. However, its weakness lies in the potential for participant dropout, which can skew results and complicate data interpretation.
Agency and Mental Health
The concept of 'agency' in mental health refers to an individual's ability to make choices and exert control over their lives. Developing a sense of agency is crucial for teenagers, as it empowers them to navigate challenges and build resilience against external pressures. Support from parents, educators, and communities plays a pivotal role in nurturing a sense of agency among young people.
Supporting Young People: Developing a Sense of Agency
Supporting young people in developing their sense of agency involves providing them with opportunities to make decisions and take on responsibilities. Programs in schools that foster leadership skills, critical thinking, and problem-solving can enable teenagers to feel more in control of their lives. Encouragement and guidance in these settings can be incredibly beneficial in promoting mental well-being.
Preventive Measures in Schools
Schools can implement several preventive measures to mitigate social media's negative impacts on mental health. Incorporating digital literacy programs that educate students about the responsible use of social media and its potential effects can be a proactive approach. Schools might also integrate mental health education that draws on psychological theories, such as cognitive-behavioral approaches, to help students develop coping mechanisms and resilience.
Future Research Directions
To develop a comprehensive understanding of the mental health challenges faced by adolescents in the context of social media, further research is essential. Areas such as the role of peer influence, the impact of cyberbullying, and the specific psychological effects of emerging social media trends require deeper investigation. Understanding these factors can equip educators, parents, and policymakers with the tools needed to support today's teenagers effectively.
In conclusion, while the study provides valuable insights into how social media use correlates with mental health issues among teenagers, it also highlights the complexity of drawing conclusions and the necessity for ongoing research. By addressing these challenges with informed and empathetic strategies, we can better support the next generation in navigating the digital landscape while safeguarding their mental health.
출처 : Original Source